The Diagnosis of Mineral Deficiencies in Plants by Visual Symptoms
by Thomas Wallace, M.C., D.Sc., A.I.C.
London — Published by His Majesty's Stationary Office — 1943
— Crown Copyright Reserved —
| Index | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| Top of Page | ||
 1. Complete Nutrient Solution — Healthy growth.
1. Complete Nutrient Solution — Healthy growth.
Potato Plant in Sand Culture
Growth Normal; foliage healthy green color.
 2. Nitrogen Deficiency — Severely restricted growth, upright habit.
2. Nitrogen Deficiency — Severely restricted growth, upright habit.
Potato Plant in Sand Culture
Growth small and single thin shoots; upright habit; leaves pale green color.
 3. Phosphorus Deficiency — Restricted growth, leaves rolled forward.
3. Phosphorus Deficiency — Restricted growth, leaves rolled forward.
Potato Plant in Sand Culture
Growth small and shoots thin; upright habit; leaves slightly pale, with
forward roll and scorched margins; defoliation of oldest leaves.
 4. Calcium Deficiency — Tip leaves small, rolled and scorched.
4. Calcium Deficiency — Tip leaves small, rolled and scorched.
Potato Plant in Sand Culture
Growth fairly good; young leaves chlorotic, forward roll and marginal
scorch. This plant failed to form tubers of appreciable size.
 5. Magnesium Deficiency — Chlorosis and necrosis of leaves,
defoliation.
5. Magnesium Deficiency — Chlorosis and necrosis of leaves,
defoliation.
Potato Plant in Sand Culture
Growth fairly good; foliage chlorotic and with intervenal necrosis; death
of older foliage and severe defoliation.
 6. Potassium Deficiency — Marginal leaf scorch.
6. Potassium Deficiency — Marginal leaf scorch.
Potato Plant in Sand Culture
Growth fairly good; leaves bluish-green and intervenal chlorosis, spotting
and marginal scorch present.
 7. Apple Leaves — No mineral deficiencies.
7. Apple Leaves — No mineral deficiencies.
Stages in development of natural autumn tints.
 8. Wheat, Young Plants — Purpling and withering of leaves.
8. Wheat, Young Plants — Purpling and withering of leaves.
Phosphorus Deficiency
Older leaves purple tinting and dying off.
 9. Oat Stems — Purpling.
9. Oat Stems — Purpling.
Phosphorus Deficiency
Leaf sheaths strong purple tints.
 10. Barley Stems — Purpling.
10. Barley Stems — Purpling.
Phosphorus Deficiency
Stems bluish green and leaf sheaths strong purple tints.
 11. Barley Heads — Purpling of beard.
11. Barley Heads — Purpling of beard.
Phosphorus Deficiency
Beards strong purple tints.
 12. Marrow Stem Kale Plant — Purpling of leaves.
12. Marrow Stem Kale Plant — Purpling of leaves.
Phosphorus Deficiency
Growth thin and upright; older leaves purple and reddish purple tints.
 13. Rape Plant — Purple and red tinting of leaves.
13. Rape Plant — Purple and red tinting of leaves.
Phosphorus Deficiency
Older leaves strong purple and red tints.
 14. Brussels Sprout Plant — Purpling of leaves.
14. Brussels Sprout Plant — Purpling of leaves.
Phosphorus Deficiency
Plant has remained stunted; leaves bluish-green with dull purple tints.
 15. Swede Leaves — Purpling.
15. Swede Leaves — Purpling.
Phosphorus Deficiency
Swede leaves. Dull purple and reddish purple tints, mainly near margins.
 16. Sugar Beet Plant — Leaves dull green, faint bronzing and purple
spotting.
16. Sugar Beet Plant — Leaves dull green, faint bronzing and purple
spotting.
Phosphorus Deficiency
Leaves green, lack luster, slight bronzing and purple spotting near margins.
 17. Potato Stem — Defoliation of older leaves and marginal scorching
of younger leaves.
17. Potato Stem — Defoliation of older leaves and marginal scorching
of younger leaves.
Phosphorus Deficiency
Potato Foliage. Leaves green, lack luster, margins scorched and curled
towards upper surfaces.
 18. Maize Plant — Purpling of leaves.
18. Maize Plant — Purpling of leaves.
Phosphorus Deficiency
Leaves strong purple tints.
 19. Apple Leaves — Typical bronzing.
19. Apple Leaves — Typical bronzing.
Phosphorus Deficiency
Dull purple and bronze tints.
 20. Gooseberry Shoot — Purpling of leaves.
20. Gooseberry Shoot — Purpling of leaves.
Phosphorus Deficiency
Leaves dull purple tints, becoming red later.
 21. Marrow Stem Kale — Forward rolling of leaves, chlorosis and ragged
leaf margins.
21. Marrow Stem Kale — Forward rolling of leaves, chlorosis and ragged
leaf margins.
Calcium Deficiency
Leaves curled forward, margins white bands, later scorched and ragged.
 22. Savoy Cabbage — Forward rolling of leaves, chlorosis and ragged leaf
margins.
22. Savoy Cabbage — Forward rolling of leaves, chlorosis and ragged leaf
margins.
Calcium Deficiency
Leaves curled forward, margins white bands, later scorched and ragged.
 23. Turnip — Marginal leaf scorch.
23. Turnip — Marginal leaf scorch.
Calcium Deficiency
Leaves curled forward, margins pale yellow bands, widening later and becoming
brown and scorched; scorched portions curl sharply over towards upper
surface.
 24. Sugar Beet — Forward rolling of leaves and ragged, scorched leaf
margins.
24. Sugar Beet — Forward rolling of leaves and ragged, scorched leaf
margins.
Calcium Deficiency
Leaves curled forward; margins scorched and ragged.
 25. Cauliflower Plant — Chlorotic "marbling" and high tints.
25. Cauliflower Plant — Chlorotic "marbling" and high tints.
Magnesium Deficiency
Older leaves highly tinted in intervenal areas; cream chlorotic marbling
and orange, red and purple tints.
 26. Cauliflower Seedlings — Tinting of older leaves.
26. Cauliflower Seedlings — Tinting of older leaves.
Magnesium Deficiency
Older leaves high yellow, red and purple tints.
 27. Cauliflower Field at Cutting Time — Chlorosis and tinting.
27. Cauliflower Field at Cutting Time — Chlorosis and tinting.
Magnesium Deficiency
Older leaves strong marbling and tinting.
 28. Broccoli Leaves — Chlorotic "marbling" and tinting.
28. Broccoli Leaves — Chlorotic "marbling" and tinting.
Magnesium Deficiency
Strong marbling and tinting as for cauliflower.
 29. Swede Leaves (Late Stage) — Intervenal red "marbling".
29. Swede Leaves (Late Stage) — Intervenal red "marbling".
Magnesium Deficiency
Red intervenal tinting following chlorotic marbling.
 30. Sugar Beet Leaves — Intervenal chlorosis and marginal necrosis.
30. Sugar Beet Leaves — Intervenal chlorosis and marginal necrosis.
Magnesium Deficiency
Intervenal chlorosis, beginning at margins and progressing towards midrib;
chlorosis followed by marginal and intervenal necrosis.
 31. Sugar Beet Plant (in situ) — Intervenal chlorosis and necrosis
older leaves.
31. Sugar Beet Plant (in situ) — Intervenal chlorosis and necrosis
older leaves.
Magnesium Deficiency
Older leaves severe intervenal chlorosis and necrosis.
 32. Sugar Beet Plants — General Field View-Intervenal chlorosis and
necrosis older leaves.
32. Sugar Beet Plants — General Field View-Intervenal chlorosis and
necrosis older leaves.
Magnesium Deficiency
Chlorosis, necrosis and dropping of older leaves.
 33. Garden Beet Plant — Intervenal chlorosis and tinting older leaves.
33. Garden Beet Plant — Intervenal chlorosis and tinting older leaves.
Magnesium Deficiency
Older leaves, intervenal chlorosis and reddish tinting.
 34. Potato Leaf — Leaflets central intervenal necrosis and marginal
"blight" attack.
34. Potato Leaf — Leaflets central intervenal necrosis and marginal
"blight" attack.
Magnesium Deficiency
Leaflets central intervenal necrosis and marginal "blight" attack
(Phytophthora infestans).
 35. Potato Shoot (var. Sharpes Express) — Tip foliage showing marginal
and intervenal necrosis.
35. Potato Shoot (var. Sharpes Express) — Tip foliage showing marginal
and intervenal necrosis.
Magnesium Deficiency
Leaflets marginal and intervenal chlorosis.
 36. Potato Plant (var. Dunbar Rover) — Chlorosis and central
intervenal leaf necrosis.
36. Potato Plant (var. Dunbar Rover) — Chlorosis and central
intervenal leaf necrosis.
Magnesium Deficiency
Chlorosis and central intervenal necrosis, beginning at oldest leaves.
 37. Potato-Field View — Chlorosis and central leaf necrosis.
37. Potato-Field View — Chlorosis and central leaf necrosis.
Magnesium Deficiency
Older foliage showing severe chlorosis and central intervenal necrosis.
 38. Tomato Leaf — Chlorotic pattern.
38. Tomato Leaf — Chlorotic pattern.
Magnesium Deficiency
Central intervenal chlorotic yellowing of leaflets.
 39. Tomato Plants in Sand Culture — Early stage of chlorosis of lower
leaves.
39. Tomato Plants in Sand Culture — Early stage of chlorosis of lower
leaves.
Magnesium Deficiency
Severe chlorotic yellowing of oldest leaves; chlorosis progressing to younger foliage.
 40. Hop Leaf — Intervenal necrosis.
40. Hop Leaf — Intervenal necrosis.
Magnesium Deficiency
Marginal and intervenal yellowing and necrosis.
 41. Apple Tree — Defoliation of shoots.
41. Apple Tree — Defoliation of shoots.
Magnesium Deficiency
Defoliation of terminal shoots progressing from base to tip.
 42. Apple Leaves (var. Lane's Prince Albert) — Chlorosis and central
intervenal necrosis.
42. Apple Leaves (var. Lane's Prince Albert) — Chlorosis and central
intervenal necrosis.
Magnesium Deficiency
Intervenal chlorosis and necrosis.
 43. Apple Leaves (var. Cox Orange Pippin) — Central intervenal
necrosis.
43. Apple Leaves (var. Cox Orange Pippin) — Central intervenal
necrosis.
Magnesium Deficiency
Central intervenal necrosis.
 44. Apple Leaves — Purpling and intervenal necrosis from marginal
areas.
44. Apple Leaves — Purpling and intervenal necrosis from marginal
areas.
Magnesium Deficiency
Purple tinting and intervenal necrosis developing from marginal areas.
 45. Gooseberry Branch — Marginal leaf coloration.
45. Gooseberry Branch — Marginal leaf coloration.
Magnesium Deficiency
Leaves broad red marginal bands which fade to cream color.
 46. Gooseberry and Black Currant Leaves — Leaf colorations.
46. Gooseberry and Black Currant Leaves — Leaf colorations.
Magnesium Deficiency
Gooseberry leaves: broad red marginal bands. Black Current leaves: purple
centers and green margins.
 47. Barley Plants — Tillering and leaf spot attack.
47. Barley Plants — Tillering and leaf spot attack.
Potassium Deficiency
Tillering excessive; leaves bluish-green and much dying off, beginning
near tips and margins: severe Leaf Stripe (Helminthosporium gramineum)
also present.
 48. Marrow Stem Kale Plant — Marginal leaf scorch.
48. Marrow Stem Kale Plant — Marginal leaf scorch.
Potassium Deficiency
Growth aquat; leaves bluish-green, slight chlorosis near margins; margins
scorched and curl sharply forward.
 49. Cauliflower Plants at Cutting Time — Marginal and intervenal
browning.
49. Cauliflower Plants at Cutting Time — Marginal and intervenal
browning.
Potassium Deficiency
Leaves severe marginal and intervenal scorch.
 50. Cabbage Plant — Marginal leaf scorch.
50. Cabbage Plant — Marginal leaf scorch.
Potassium Deficiency
Older leaves severe marginal scorch and forward curling of leaf margins.
 51. Swede Plant — Marginal leaf scorch and intervenal chlorosis.
51. Swede Plant — Marginal leaf scorch and intervenal chlorosis.
Potassium Deficiency
Leaves dull green with marginal and intervenal chlorosis; margins
scorched and curled forward.
 52. Sugar Beet Plant — Marginal and intervenal browning.
52. Sugar Beet Plant — Marginal and intervenal browning.
Potassium Deficiency
Older leaves severe marginal and intervenal scorch; they shrivel and
hang down limply.
 53. Mangold Plant — Marginal and intervenal browning.
53. Mangold Plant — Marginal and intervenal browning.
Potassium Deficiency
Older leaves severe marginal and intervenal scorch; They shrivel and hang
down limply around bulb.
 54. Potato Foliage — Bronzing and scorching of leaves.
54. Potato Foliage — Bronzing and scorching of leaves.
Potassium Deficiency
Bronzing and scorching of leaves.
 55. Potato Foliage — Marginal scorching and intervenal chlorosis.
55. Potato Foliage — Marginal scorching and intervenal chlorosis.
Potassium Deficiency
Intervenal chlorosis in addition to bronzing and scorching of leaves;
oldest leaves are withering.
 56. Potato Plants — Field View-Collapse of foliage and haulms.
56. Potato Plants — Field View-Collapse of foliage and haulms.
Potassium Deficiency
Collapse of haulms, withering of leaves and defoliation.
 57. Tomato Leaf — Marginal scorch following gray tints.
57. Tomato Leaf — Marginal scorch following gray tints.
Potassium Deficiency
Marginal and intervenal gray coloration followed by marginal scorching.
 58. Tomato Fruit — Blotchy uneven ripening, cracking of skin near stem.
58. Tomato Fruit — Blotchy uneven ripening, cracking of skin near stem.
Potassium Deficiency
Blotchy ripening: green and yellow areas merging into general red color of surface.
 59. Field Bean Plant — Marginal scorching of leaves.
59. Field Bean Plant — Marginal scorching of leaves.
Potassium Deficiency
Short internodes; leaves scorched and forward curled margins.
 60. Runner Bean Shoot — Marginal scorching and intervenal chlorosis
of leaves.
60. Runner Bean Shoot — Marginal scorching and intervenal chlorosis
of leaves.
Potassium Deficiency
Leaflets curled backward; strong intervenal chlorosis and brown marginal
scorch; scorched areas curled forward.
 61. Onion Plant — Die-back and browning of leaves.
61. Onion Plant — Die-back and browning of leaves.
Potassium Deficiency
Dying off of older leaves and dying back of leaves from tips.
 62. Maize Plant — Marginal scorching of leaves.
62. Maize Plant — Marginal scorching of leaves.
Potassium Deficiency
Internodes short, leaves relatively long; marginal and tip browning
of leaves.
 63. Hop Leaf — Marginal scorching.
63. Hop Leaf — Marginal scorching.
Potassium Deficiency
Slight marginal chlorosis followed by scorching.
 64. Apple Leaves — Marginal leaf scorch.
64. Apple Leaves — Marginal leaf scorch.
Potassium Deficiency
Leaves bluish-green with slight marginal and intervenal chlorosis, followed
by marginal scorching, either brown or grayish brown color.
 65. Gooseberry Leaves — Marginal leaf scorch.
65. Gooseberry Leaves — Marginal leaf scorch.
Potassium Deficiency
Leaves bluish-green, generally curled backward; developing purpling tints
followed by grayish brown marginal scorch; purpling disappears as
scorching develops.
 66. Black Currant Shoot — Leaf purpling preceding marginal scorch.
66. Black Currant Shoot — Leaf purpling preceding marginal scorch.
Potassium Deficiency
Purple tinting of leaves which precedes development of marginal scorch.
 67. Black Currant Shoot — Marginal leaf scorch.
67. Black Currant Shoot — Marginal leaf scorch.
Potassium Deficiency
Brown marginal scorch and intervenal chlorosis which follows purple tinting.
 68. Red Currant Shoot — Marginal leaf scorch and slight chlorosis.
68. Red Currant Shoot — Marginal leaf scorch and slight chlorosis.
Potassium Deficiency
Marginal leaf scorch with forward curling of margins and intervenal
chlorosis.
 69. Raspberry Leaf — Marginal leaf scorch and intervenal necrosis.
69. Raspberry Leaf — Marginal leaf scorch and intervenal necrosis.
Potassium Deficiency
Marginal leaf scorch and intervenal browning; leaves generally curl
towards under surfaces.
 70. Young Wheat Plants — Severe chlorosis beginning at tips of leaves.
70. Young Wheat Plants — Severe chlorosis beginning at tips of leaves.
Iron Deficiency
Severe chlorosis of leaves, beginning at tips; death of tips.
 71. Broccoli Plant — Chlorosis of leaves.
71. Broccoli Plant — Chlorosis of leaves.
Iron Deficiency
Chlorosis of leaves, beginning as a chlorotic motting.
 72. Savoy Cabbage Plant — Severe chlorosis of leaves.
72. Savoy Cabbage Plant — Severe chlorosis of leaves.
Iron Deficiency
Severe chlorosis of leaves, beginning as a chlorotic motting.
 73. Turnip Plant — Chlorotic mottling of leaves.
73. Turnip Plant — Chlorotic mottling of leaves.
Iron Deficiency
Chlorotic mottling of leaves.
 74. Tomato Foliage — Intervenal chlorosis and necrosis of tip foliage.
74. Tomato Foliage — Intervenal chlorosis and necrosis of tip foliage.
Iron Deficiency
Tip leaves chlorosis of leaflets, most severe near midribs and bases, followed by necrosis.
 75. Raspberry Foliage — Chlorosis of leaves.
75. Raspberry Foliage — Chlorosis of leaves.
Iron Deficiency
Tip leaves severe chlorosis followed by necrosis.
 76. Strawberry Plant — Chlorosis of leaves.
76. Strawberry Plant — Chlorosis of leaves.
Iron Deficiency
Leaves severe marginal and intervenal chlorosis.
 77. Oat Plants — Gray Speck lesions and blind panicles.
77. Oat Plants — Gray Speck lesions and blind panicles.
Manganese Deficiency
Leaves grayish-brown elongated specks and streaks, most prevalent in
basal halves; Breaking of leaves with distal areas remaining green; empty
panicles.
 78. Marrow Stem Kale Plant — Chlorotic "marbling" of leaves.
78. Marrow Stem Kale Plant — Chlorotic "marbling" of leaves.
Manganese Deficiency
Early stage of deficiency, leaves intervenal chlorotic marbling.
 79. Marrow Stem Kale Plant — Severe chlorosis.
79. Marrow Stem Kale Plant — Severe chlorosis.
Manganese Deficiency
Advanced stage of deficiency, leaves very severe chlorosis.
 80. Savoy Cabbage Plant — Chlorosis and necrosis.
80. Savoy Cabbage Plant — Chlorosis and necrosis.
Manganese Deficiency
Leaves severe intervenal chlorotic marbling and necrosis.
 81. Sugar Beet Leaf — Intervenal chlorosis (Speckled Yellows).
81. Sugar Beet Leaf — Intervenal chlorosis (Speckled Yellows).
Manganese Deficiency
Severe intervenal chlorosis, "Speckled Yellows".
 82. Sugar Beet Plant — Severe intervenal chlorosis of foliage.
82. Sugar Beet Plant — Severe intervenal chlorosis of foliage.
Manganese Deficiency
Leaves severe "Speckled Yellows" and leaf margins curled forward.
 83. Garden Beet Leaves — Intervenal speckling.
83. Garden Beet Leaves — Intervenal speckling.
Manganese Deficiency
Leaves triangular shape, margins curled forward and severe intervenal
speckling.
 84. Garden Beet Plant — Intervenal speckling.
84. Garden Beet Plant — Intervenal speckling.
Manganese Deficiency
Leaves triangular shape, margins curled forward; older leaves severely
speckled; root dwarfed.
 85. Garden Beet (General Field View) — Reddening of foliage of globe
beet.
85. Garden Beet (General Field View) — Reddening of foliage of globe
beet.
Manganese Deficiency
Foreground susceptible "globe" variety severely speckled; background
resistant "long" variety.
 86. Parsnip Leaf — Intervenal chlorosis.
86. Parsnip Leaf — Intervenal chlorosis.
Manganese Deficiency
Severe marginal and intervenal chlorosis.
 87. Potato Leaves — Black specks along veins.
87. Potato Leaves — Black specks along veins.
Manganese Deficiency
Leaves from near tips of shoots still green but showing characteristic
spotting along veins.
 88. Potato Plants (General View) — Stunted growth and chlorosis of
young foliage.
88. Potato Plants (General View) — Stunted growth and chlorosis of
young foliage.
Manganese Deficiency
Stunted growth and dying of haulm at tips; leaves pale and younger leaves
yellow or necrotic; tip leaflets small and strong forward curling of
margins.
 89. Runner Bean Leaves — Intervenal chlorosis.
89. Runner Bean Leaves — Intervenal chlorosis.
Manganese Deficiency
Leaflets intervenal chlorosis.
 90. Dwarf (French) Bean Plants — Severe chlorosis and intervenal
necrosis.
90. Dwarf (French) Bean Plants — Severe chlorosis and intervenal
necrosis.
Manganese Deficiency
Leaves severe chlorosis and necrosis.
 91. Apple Foliage (var. Cox Orange Pippin) — Marginal and intervenal
chlorosis.
91. Apple Foliage (var. Cox Orange Pippin) — Marginal and intervenal
chlorosis.
Manganese Deficiency
Leaves marginal and intervenal chlorosis.
 92. Apple Foliage (var. Early Victoria) — Severe chlorosis.
92. Apple Foliage (var. Early Victoria) — Severe chlorosis.
Manganese Deficiency
Leaves severe chlorosis; intervenal pattern less pronounced than for Cox
Orange Pippin.
 93. Apple Tree (var. Early Victoria) — Severe chlorosis.
93. Apple Tree (var. Early Victoria) — Severe chlorosis.
Manganese Deficiency
Leaves severe chlorosis over practically whole tree; young leaves of terminal
shoots not as severely affected as older leaves.
 94. Marrow Stem Kale Plant — Distortion of young foliage and crack in
stem.
94. Marrow Stem Kale Plant — Distortion of young foliage and crack in
stem.
Boron Deficiency
Distortion of young leaves, marginal mottling and external vertical crack
in stem.
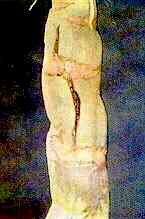 95. Marrow Stem Kale Stem — Crack in stem.
95. Marrow Stem Kale Stem — Crack in stem.
Boron Deficiency
Stem Portion. External vertical crack.
 96. Kale Stem — Longitudinal and transverse sections-Hollow center and
infection with bacillus carotovorus.
96. Kale Stem — Longitudinal and transverse sections-Hollow center and
infection with bacillus carotovorus.
Boron Deficiency
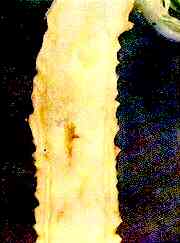 97. Savoy Cabbage Stem — Browning and necrosis of pith.
97. Savoy Cabbage Stem — Browning and necrosis of pith.
Boron Deficiency
Longitudinal Section of Stem. Necrosis and splitting of pith.
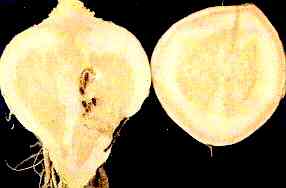 98. Swede Roots — Transverse and longitudinal sections-Brown Heart
condition.
98. Swede Roots — Transverse and longitudinal sections-Brown Heart
condition.
Boron Deficiency
Longitudinal and Transverse Sections. Water-soaked and brown areas.
"Brown Heart" condition.
 99. Swede Roots — External View – Rough skin condition.
99. Swede Roots — External View – Rough skin condition.
Boron Deficiency
Rough skin condition found accompanying "Brown Heart" but not usual.
 100. Sugar Beet, Young Plant — Small and distorted crown leaves.
100. Sugar Beet, Young Plant — Small and distorted crown leaves.
Boron Deficiency
Early stage of boron deficiency. Young leaves distorted and fail to develop.
 101. Sugar Beet, Old Plant — Old leaves scorched and wilted, cluster
of young crown leaves.
101. Sugar Beet, Old Plant — Old leaves scorched and wilted, cluster
of young crown leaves.
Boron Deficiency
Old leaves wilted, wilted, scorched and show patches of yellow pigment.
Original crown leaves have died, followed by development of numerous small
misshapen leaves from secondary growing points.
 102. Sugar Beet — Heart Rot (boron deficiency) and Intervenal
Chlorosis (manganese deficiency).
102. Sugar Beet — Heart Rot (boron deficiency) and Intervenal
Chlorosis (manganese deficiency).
Boron And Manganese Deficiency
Boron deficiency shown by "Crown Rot"; manganese deficiency by speckled
condition of leaves ("Speckled Yellows").
 103. Mangold Plant (in situ) — Cluster of crown leaves and rotting
of root.
103. Mangold Plant (in situ) — Cluster of crown leaves and rotting
of root.
Boron Deficiency
Development of leaves from secondary growing points on crown and rotting of
root at side.
 104. Mangold Plant — Rotting of crown and rough condition of petiole
epidermis.
104. Mangold Plant — Rotting of crown and rough condition of petiole
epidermis.
Boron Deficiency
Typical case of "Crown Rot". Petioles of leaves show cracking of epidermis
on upper surfaces.
 105. Mangold Plants — Rotting of crown leaves and roots.
105. Mangold Plants — Rotting of crown leaves and roots.
Boron Deficiency
Death of foliage and rotting of roots.
 106. Table Beet Plants — External view of "Canker".
106. Table Beet Plants — External view of "Canker".
Boron Deficiency
Death of foliage and rotting of outer tissues of the roots ("Canker").
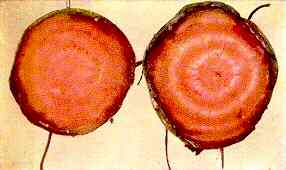 107. Table Beet Plants — Cross section of roots showing superficial
"Canker".
107. Table Beet Plants — Cross section of roots showing superficial
"Canker".
Boron Deficiency
Transverse Section through Canker Area. "Canker" lesions restricted to
outer tissues; may spread towards center later.
 108. Potato Foliage — Boron toxicity effects, marginal browning.
108. Potato Foliage — Boron toxicity effects, marginal browning.
Toxic effects show as narrow brown, marginal rims on leaflets.
 109. Potato Foliage — Boron toxicity (marginal browning) and magnesium
deficiency (intervenal necrosis).
109. Potato Foliage — Boron toxicity (marginal browning) and magnesium
deficiency (intervenal necrosis).
Boron Toxicity And Magnesium Deficiency
Boron toxicity shown by narrow brown marginal rims on leaflets;
magnesium deficiency by intervenal necrosis.
 110. Sugar Beet Leaves — Virus Yellows, intervenal chlorosis
(cf.
Plate No. 30, intervenal chlorosis, magnesium deficiency).
110. Sugar Beet Leaves — Virus Yellows, intervenal chlorosis
(cf.
Plate No. 30, intervenal chlorosis, magnesium deficiency).
"Virus Yellows" of Sugar Beet
Leaves intervenal "yellowing" in asymmetrical patches; yellow patches
brittle and crackle when squeezed in the hand. May be confused with
magnesium deficiency symptoms. (cf.
Plate No. 30)
 111. Sugar Beet Plant — Virus Yellows (cf.
Plate No. 31, intervenal
chlorosis, magnesium deficiency)
111. Sugar Beet Plant — Virus Yellows (cf.
Plate No. 31, intervenal
chlorosis, magnesium deficiency)
"Virus Yellows" of sugar beet
Leaves upright, "yellowing" in patches and often most severe near tips. (cf.
Plate No. 31, magnesium deficient plant)
 112. Cabbage Plant — Insect injury to terminal bud (cf.
Plate No. 94, Kale,
distortion, boron deficiency)
112. Cabbage Plant — Insect injury to terminal bud (cf.
Plate No. 94, Kale,
distortion, boron deficiency)
Insect Damage (Root Flies, Weevils, etc.)
Injury to growing point and distortion of leaves, may be confused with boron
deficiency.
 113. Turnip Plant — Insect injury to laminae and petioles of leaves
(cf.
Plate No. 104,
Mangold, distortion and petiole roughening, boron, deficiency)
113. Turnip Plant — Insect injury to laminae and petioles of leaves
(cf.
Plate No. 104,
Mangold, distortion and petiole roughening, boron, deficiency)
Insect Damage (Root Flies, Weevils, etc.)
Distortion of foliage and injury to petioles, may be confused with boron
deficiency.
 114. Red Currant — Chloride injury (cf.
Plate No. 68, leaf scorch, potassium
deficiency)
114. Red Currant — Chloride injury (cf.
Plate No. 68, leaf scorch, potassium
deficiency)
Chloride Injury
Marginal scorching may be confused with leaf scorch due to potassium
deficiency. (cf.
Plate No. 68)
Using Hydroponics to Understand the Earth's Life Processes
on the Atomic Level
The Tortoise Shell Hydroponic Reference Center
Understanding Colloidal Suspensions
Plants need to absorb what you feed them.
" The Art of Healing Ourselves "
Only You can bring Good Health and Healing into Your Body.