The Diagnosis of Mineral Deficiencies in Plants by Visual Symptoms
Published by His Majesty's Stationary Office — 1943
— Crown Copyright Reserved —
BEANS IN SAND CULTURE — from the 1951 edition
by Thomas Wallace, M.C., D.Sc., A.I.C.
 173. Broad Bean Plants
173. Broad Bean Plants
Phosphorus deficiency
Stems thin, leaves erect; early defoliation of basal leaves.
 174. Broad Bean Plants
174. Broad Bean Plants
Calcium deficiency
Young growth deformed, young stems and petioles wilt and growing points die;
leaflets near growing points fail to expand, distorted and hooked,
and tips die.
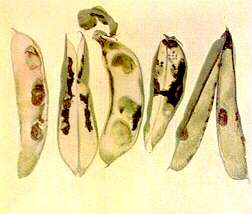 175. Broad Bean Pods and Seeds
175. Broad Bean Pods and Seeds
Calcium deficiency
Pods deformed, wilted and blackened; seeds fail to develop.
 176. Broad Bean Leaves
176. Broad Bean Leaves
Magnesium deficiency
Central intervenal chlorosis, margins green.
 177. Broad Bean Shoot
177. Broad Bean Shoot
Potassium deficiency
Internodes short; leaves dark brown marginal scorch and margins curled
forward.
 178. Broad Bean Seeds
178. Broad Bean Seeds
Manganese deficiency
Brown lesions in centers of cotyledons, similar "Marsh Spot" in peas. (cf.
Plate No. 204)
 179. Broad Bean Plants
179. Broad Bean Plants
Boron deficiency
Stems somewhat stiff; growing points die and lateral growths develop from
bases of shoots; leaves slight intervenal chlorosis.
 180. Dwarf (French) Bean Plants
180. Dwarf (French) Bean Plants
Nitrogen deficiency
Growth dwarfed and thin; leaves pale green and older leaves yellow and
die early.
 181. Dwarf Bean Plants
181. Dwarf Bean Plants
Phosphorus deficiency
Growth dwarfed and thin: leaves dark, lustreless green, older leaves
turn brown and shed early.
 182. Dwarf Bean Plants
182. Dwarf Bean Plants
Calcium deficiency
Growth dwarfed and thin; stems, petioles, pedicels and pods wilted;
early defoliation.
 183. Dwarf Bean Pods
183. Dwarf Bean Pods
Calcium deficiency
Pods wilted and deformed; seeds fail to develop.
 184. Dwarf Bean Foliage
184. Dwarf Bean Foliage
Magnesium deficiency
Older leaves chlorotic mottling, followed by general yellowing and
brown necrotic spotting.
 185. Dwarf Beans Leaf
185. Dwarf Beans Leaf
Potassium deficiency
Intervenal chlorosis near margins followed by marginal scorch.
 186. Dwarf Bean Plants
186. Dwarf Bean Plants
Manganese deficiency
Leaves severe chlorosis and necrosis.
 187. Dwarf Bean Plants
187. Dwarf Bean Plants
Boron deficiency
Stems abnormally thickened; longitudinal splitting of epicotyl;
death of growing point; leaves some chlorosis.
 188. Haricot Bean Plants
188. Haricot Bean Plants
Manganese deficiency
Leaves strong chlorotic motting.
 189. Haricot Bean Seeds
189. Haricot Bean Seeds
Manganese deficiency
Brown lesions in cotyledons, similar "Marsh Spot" of peas (cf.
Plate No. 204)
 190. Runner Bean Plant
190. Runner Bean Plant
Nitrogen deficiency
Growth stunted and thin; leaves pale green and older leaves yellow and
die early; stems and petioles tend to be tinted red.
 191. Runner Bean Leaves
191. Runner Bean Leaves
Calcium deficiency
Leaves pale green, tips and margins of leaflets chlorotic patches and
brown spots.
 192. Runner Bean Leaf
192. Runner Bean Leaf
Magnesium deficiency
Leaflets slightly pale and striking intervenal necrosis.
 193. Runner Bean Foliage
193. Runner Bean Foliage
Potassium deficiency
Leaflets curled backward; intervenal chlorosis and brown marginal scorch;
scorched margins curled forward.
 194. Runner Bean Leaves
194. Runner Bean Leaves
Manganese deficiency
Leaflets intervenal chlorotic motting. (cf.
Plate No. 196, manganese toxicity)
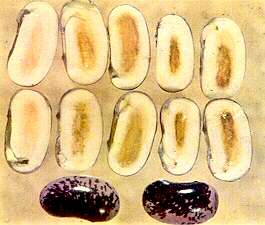 195. Runner Bean Seeds
195. Runner Bean Seeds
Manganese deficiency
Brown lesions in cotyledons, similar to "Marsh Spot" of peas. (cf.
Plate No. 204)
 196. Runner Bean Plant
196. Runner Bean Plant
Manganese toxicity (soil acidity complex)
Leaves intervenal chlorosis beginning at margins, followed by brown
necrotic spotting (cf.
Plate No. 194)
 197. Runner Bean Leaves
197. Runner Bean Leaves
Manganese toxicity (soil acidity complex)
Intervenal chlorosis and fine necrotic brown spotting.
 198. Runner Bean Stem and Leaves
198. Runner Bean Stem and Leaves
Boron deficiency
Stem thickened and stiff; growing points die; leaves slight chlorotic
mottling.
| Index | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| Top of Page | ||
Color Pictures of Mineral Defeciencies in Plants – 1943
Using Hydroponics to Understand the Earth's Life Processes
Understanding Colloidal Suspensions
" The Art of Healing Ourselves "
The Diagnosis of Mineral Deficiencies in Plants by Visual Symptoms
by Thomas Wallace, M.C., D.Sc., A.I.C.
on the Atomic Level
The Tortoise Shell Hydroponic Reference Center
Plants need to absorb what you feed them.
Only You can bring Good Health and Healing into Your Body.